The OS module in Python provides functions for interacting with the operating system. OS comes under Python’s standard utility modules. This module provides a portable way of using operating system-dependent functionality.
The *os* and *os.path* modules include many functions to interact with the file system.
Python-OS-ModuleFunctions
Here we will discuss some important functions of the Python os module :
- Handling the Current Working Directory
- Creating a Directory
- Listing out Files and Directories with Python
- Deleting Directory or Files using Python
Handling the Current Working Directory
Consider Current Working Directory(CWD) as a folder, where Python is operating. Whenever the files are called only by their name, Python assumes that it starts in the CWD which means that name-only reference will be successful only if the file is in the Python’s CWD.
Note: The folder where the Python script is running is known as the Current Directory. This is not the path where the Python script is located.
Getting the Current working directory
To get the location of the current working directory os.getcwd() is used.
Example: This code uses the ‘os' module to get and print the current working directory (CWD) of the Python script. It retrieves the CWD using the ‘os.getcwd()' and then prints it to the console.
import os cwd = os.getcwd() print("Current working directory:", cwd)
Output:
Current working directory: /home/nikhil/Desktop/gfg
Changing the Current working directory
To change the current working directory(CWD) os.chdir() method is used. This method changes the CWD to a specified path. It only takes a single argument as a new directory path.
Note: The current working directory is the folder in which the Python script is operating.
Example: The code checks and displays the current working directory (CWD) twice: before and after changing the directory up one level using os.chdir('../'). It provides a simple example of how to work with the current working directory in Python.
import os def current_path(): print("Current working directory before") print(os.getcwd()) print() current_path() os.chdir('../') current_path()
Output:
Current working directory before
C:\Users\Nikhil Aggarwal\Desktop\gfg
Current working directory after
C:\Users\Nikhil Aggarwal\Desktop
Creating a Directory
There are different methods available in the OS module for creating a directory. These are –
- os.mkdir()
- os.makedirs()
Using os.mkdir()
By using os.mkdir() method in Python is used to create a directory named path with the specified numeric mode. This method raises FileExistsError if the directory to be created already exists.
Example: This code creates two directories: “GeeksforGeeks” within the “D:/Pycharm projects/” directory and “Geeks” within the “D:/Pycharm projects” directory.
- The first directory is created using the
os.mkdir()method without specifying the mode. - The second directory is created using the same method, but a specific mode (
0o666) is provided, which grants read and write permissions. - The code then prints messages to indicate that the directories have been created.
import osdirectory = "GeeksforGeeks"parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/"path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)os.mkdir(path)print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)directory = "Geeks"parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects"mode = 0o666path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)os.mkdir(path, mode)print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
Output:
Directory 'GeeksforGeeks' created
Directory 'Geeks' created
Using os.makedirs()
os.makedirs() method in Python is used to create a directory recursively. That means while making leaf directory if any intermediate-level directory is missing, os.makedirs() method will create them all.
Example:This code creates two directories, “Nikhil” and “c”, within different parent directories. It uses the os.makedirs function to ensure that parent directories are created if they don’t exist.
It also sets the permissions for the “c” directory. The code prints messages to confirm the creation of these directories
import osdirectory = "Nikhil"parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksForGeeks/Authors"path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)os.makedirs(path)print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)directory = "c"parent_dir = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksforGeeks/a/b"mode = 0o666path = os.path.join(parent_dir, directory)os.makedirs(path, mode)print("Directory '% s' created" % directory)
Output:
Directory 'Nikhil' created
Directory 'c' created
Listing out Files and Directories with Python
There is os.listdir() method in Python is used to get the list of all files and directories in the specified directory. If we don’t specify any directory, then the list of files and directories in the current working directory will be returned.
Example: This code lists all the files and directories in the root directory (“/”). It uses the os.listdir function to get the list of files and directories in the specified path and then prints the results.
import os path = "/"dir_list = os.listdir(path) print("Files and directories in '", path, "' :") print(dir_list)
Output:
Files and directories in ' / ' :
['sys', 'run', 'tmp', 'boot', 'mnt', 'dev', 'proc', 'var', 'bin', 'lib64', 'usr',
'lib', 'srv', 'home', 'etc', 'opt', 'sbin', 'media']
Deleting Directory or Files using Python
OS module provides different methods for removing directories and files in Python. These are –
- Using os.remove()
- Using os.rmdir()
Using os.remove() Method
os.remove() method in Python is used to remove or delete a file path. This method can not remove or delete a directory. If the specified path is a directory then OSError will be raised by the method.
Example: Suppose the file contained in the folder are:
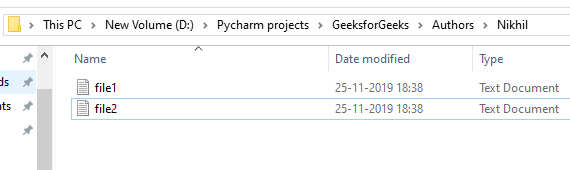
This code removes a file named “file1.txt” from the specified location “D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksforGeeks/Authors/Nikhil/”. It uses the os.remove function to delete the file at the specified path.
import os file = 'file1.txt'location = "D:/Pycharm projects/GeeksforGeeks/Authors/Nikhil/"path = os.path.join(location, file) os.remove(path)
Output:
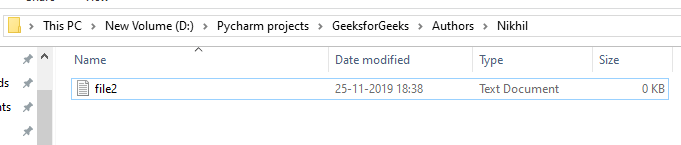
Using os.rmdir()
os.rmdir() method in Python is used to remove or delete an empty directory. OSError will be raised if the specified path is not an empty directory.
Example: Suppose the directories are
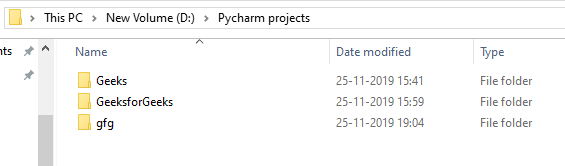
This code attempts to remove a directory named “Geeks” located at “D:/Pycharm projects/”.
It uses the os.rmdir function to delete the directory. If the directory is empty, it will be removed. If it contains files or subdirectories, you may encounter an error.
import os directory = "Geeks"parent = "D:/Pycharm projects/"path = os.path.join(parent, directory) os.rmdir(path)
Output:

Commonly Used Functions
Using os.name function
This function gives the name of the operating system dependent module imported. The following names have currently been registered: ‘posix’, ‘nt’, ‘os2’, ‘ce’, ‘java’ and ‘riscos’.
import osprint(os.name)
Output:
posix
Note: It may give different output on different interpreters, such as ‘posix’ when you run the code here.
Using os.error Function
All functions in this module raise OSError in the case of invalid or inaccessible file names and paths, or other arguments that have the correct type, but are not accepted by the operating system. os.error is an alias for built-in OSError exception.
This code reads the contents of a file named ‘GFG.txt’. It uses a ‘try…except‘ block to handle potential errors, particularly the ‘IOError‘ that may occur if there’s a problem reading the file.
If an error occurs, it will print a message saying, “Problem reading: GFG.txt.”
import ostry: filename = 'GFG.txt' f = open(filename, 'rU') text = f.read() f.close()except IOError: print('Problem reading: ' + filename)
Output:
Problem reading: GFG.txt
Using os.popen() Function
This method opens a pipe to or from command. The return value can be read or written depending on whether the mode is ‘r’ or ‘w’.
Syntax:
os.popen(command[, mode[, bufsize]])
Parameters mode & bufsize are not necessary parameters, if not provided, default ‘r’ is taken for mode.
This code opens a file named ‘GFG.txt’ in write mode, writes “Hello” to it, and then reads and prints its contents. The use of os.popen is not recommended, and standard file operations are used for these tasks.
import osfd = "GFG.txt"file = open(fd, 'w')file.write("Hello")file.close()file = open(fd, 'r')text = file.read()print(text)file = os.popen(fd, 'w')file.write("Hello")
Output:
Hello
Note: Output for popen() will not be shown, there would be direct changes into the file.
Using os.close() Function
Close file descriptor fd. A file opened using open(), can be closed by close()only. But file opened through os.popen(), can be closed with close() or os.close(). If we try closing a file opened with open(), using os.close(), Python would throw TypeError.
import osfd = "GFG.txt"file = open(fd, 'r')text = file.read()print(text)os.close(file)
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\GFG\Desktop\GeeksForGeeksOSFile.py", line 6, in
os.close(file)
TypeError: an integer is required (got type _io.TextIOWrapper)
Note: The same error may not be thrown, due to the non-existent file or permission privilege.
Using os.rename() Function
A file old.txt can be renamed to new.txt, using the function os.rename(). The name of the file changes only if, the file exists and the user has sufficient privilege permission to change the file.
import osfd = "GFG.txt"os.rename(fd,'New.txt')os.rename(fd,'New.txt')
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\GFG\Desktop\ModuleOS\GeeksForGeeksOSFile.py", line 3, in
os.rename(fd,'New.txt')
FileNotFoundError: [WinError 2] The system cannot find the
file specified: 'GFG.txt' -> 'New.txt'
A file name “GFG.txt” exists, thus when os.rename() is used the first time, the file gets renamed.
Upon calling the function os.rename() second time, file “New.txt” exists and not “GFG.txt” thus Python throws FileNotFoundError.
Using os.remove() Function
Using the Os module we can remove a file in our system using the os.remove() method. To remove a file we need to pass the name of the file as a parameter.
import os #importing os module.os.remove("file_name.txt") #removing the file.
The OS module provides us a layer of abstraction between us and the operating system.
When we are working with os module always specify the absolute path depending upon the operating system the code can run on any os but we need to change the path exactly. If you try to remove a file that does not exist you will get FileNotFoundError.
Using os.path.exists() Function
This method will check whether a file exists or not by passing the name of the file as a parameter. OS module has a sub-module named PATH by using which we can perform many more functions.
import os #importing os moduleresult = os.path.exists("file_name") #giving the name of the file as a parameter.print(result)
Output:
False
As in the above code, the file does not exist it will give output False. If the file exists it will give us output True.
Using os.path.getsize() Function
In os.path.getsize() function, python will give us the size of the file in bytes. To use this method we need to pass the name of the file as a parameter.
import os #importing os modulesize = os.path.getsize("filename")print("Size of the file is", size," bytes.")
Output:
Size of the file is 192 bytes.
P
Piyush Doorwar
Improve
Previous Article
OS Module in Python with Examples
Next Article
Generating Random id's using UUID in Python